Carolina Olid
(Assistant professor)
Email: carolina.olid.garcia@slu.se
Research Summary
My primary research goals are directed towards evaluating human and climate impact on ecological and biogeochemical processes using radionuclides as tracers. I have expertise in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems at various temporal and spatial scales. I am interested on climate change in boreal and arctic ecosystems where I model elemental (carbon, metals, nutrients) fluxes within soils, peatlands and lakes and their response to environmental stressors such as increasing temperatures or pollutants deposition.
Current Projects
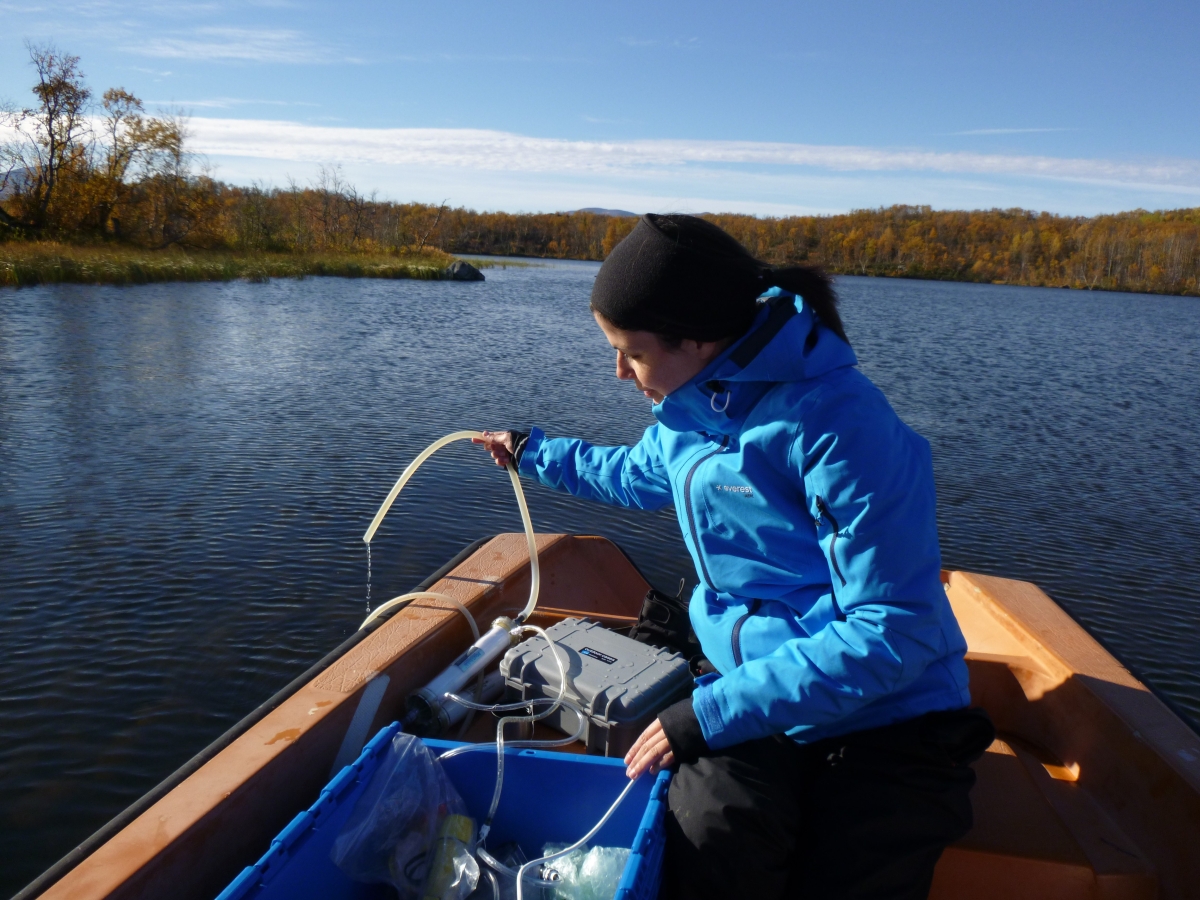
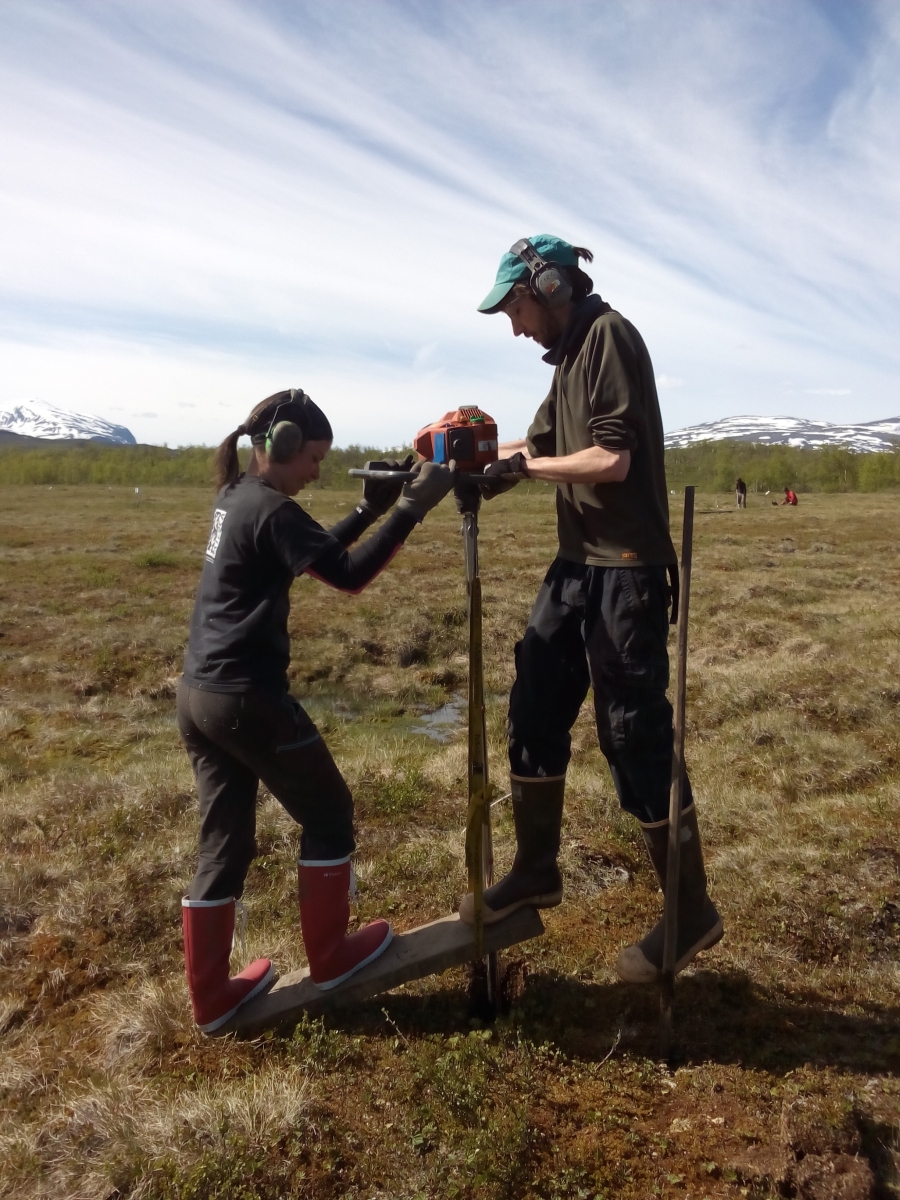
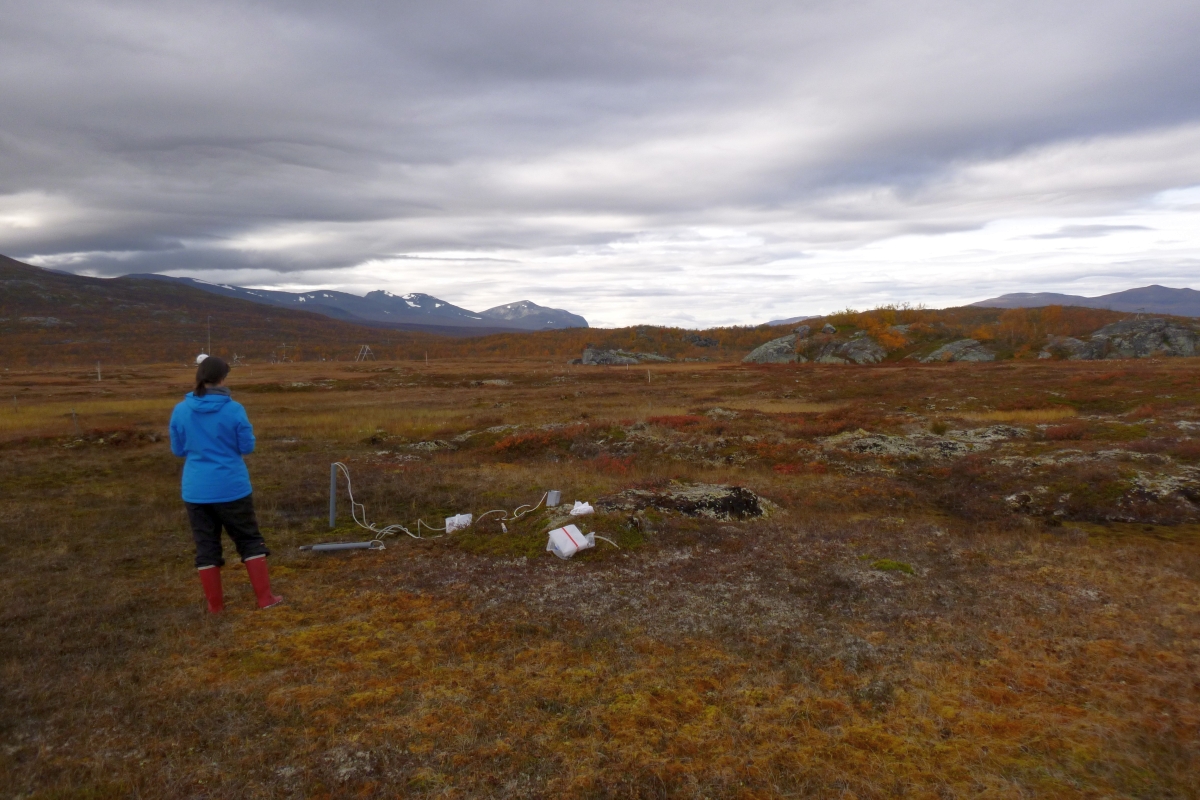
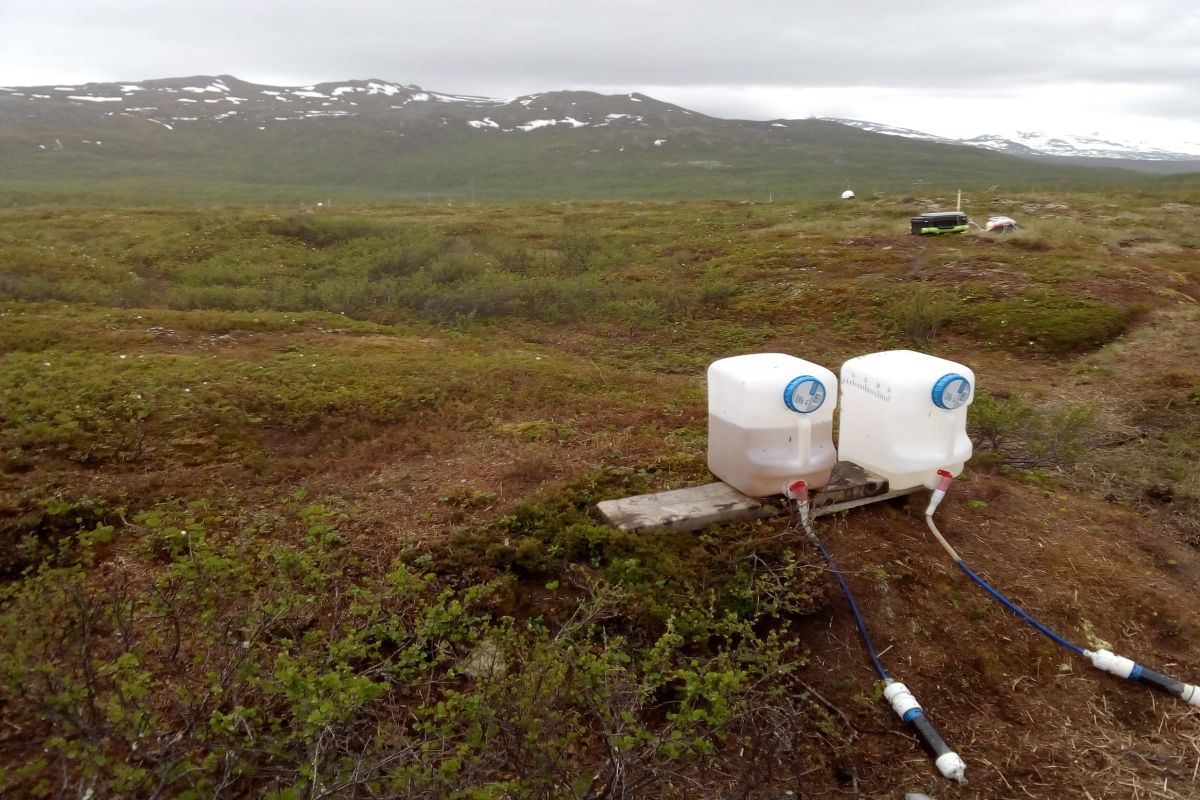
Photos From the Field